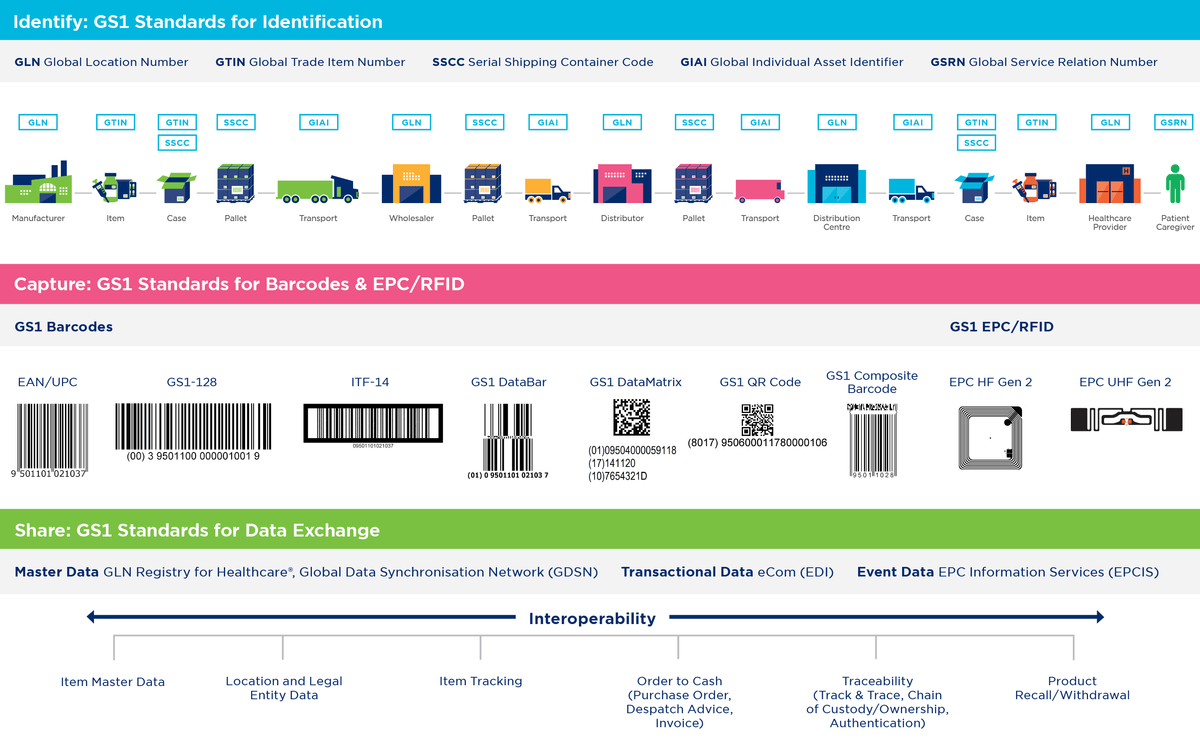
GS1 Standards are open, global, proven and simple.
- Open, technology-independent standards permit full interoperability and compatibility. End users are not locked into proprietary solutions and R&D resources can be released up for other added value developments once standards have been adopted.
- Healthcare is by nature a global sector, with supply chains that often cross borders. A global standardised system for traceability, from product manufacture to patient treatment, is imperative to comply with the increasing legal requirements for product traceability around the world. In cases of cross border trading, a global trade item number (GTIN) can be used to identify that product in any country without any restrictions or errors.
- The GS1 system of standards is a system that has proven its robustness over the last 30+ years in different sectors worldwide.
- Standards must be simple to be useable by all players in the supply chain and not give undue advantage to certain players through complexity.
Adoption and implementation of GS1 AIDC
Automatic identification systems (barcode or RFID) can have a very wide range of applications, including point-of-care scanning to match product data to patient data, verification of patient identity via a wristband, enabling the introduction of robotic dispensing systems, recording implant serial numbers in patient records and central registries, tracking and tracing of individual instruments through decontamination, stock control and supplies management, tracking assets throughout a network of facilities, …
All these applications and systems enable the realisation of associated health and economic benefits: reducing medication errors, preventing counterfeiting, saving costs and increasing the Healthcare supply chain efficiency and transparency.
Numerous studies have shown that automatic identification throughout the entire Healthcare supply chain, right to the point of delivery to the patient, is an extremely effective tool in preventing medication errors.
However, global standards are needed for an effective and efficient roll-out of automatic identification systems in the healthcare sector.
Application sandard, which provides a common set of data and data carriers for medical products at every packaging level, including specific guidance on selection and use of product identification keys, additional product and production data [for example; lot number, expiration date, and/or serial number (where applicable)], and data carriers
- Automatic Identification and Data Capture (AIDC) Application Standard for Small Instruments, which specifically covers the marking of surgical instruments to enable traceability throughout the instrument reprocessing cycle, and in particular to and from the sterilisation department.